Vitamin C
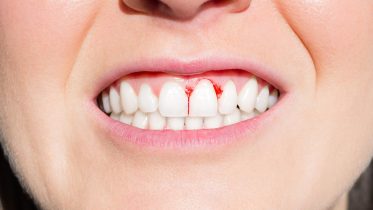
Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, and also sold as a dietary supplement. It is used to prevent and treat scurvy. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient involved in the repair of tissue, the formation of collagen, and the enzymatic production of certain neurotransmitters. It is required for the functioning of several enzymes and is important for immune system function. It also functions as an antioxidant. Most animals are able to synthesize their own vitamin C. However, apes and monkeys, most bats, some rodents, and certain other animals must acquire it from dietary sources. There is some evidence that regular use of supplements may reduce the duration of the common cold, but it does not appear to prevent infection. It is unclear whether supplementation affects the risk of cancer, cardiovascular disease, or dementia. It may be taken by mouth or by injection. Vitamin C is generally well tolerated.