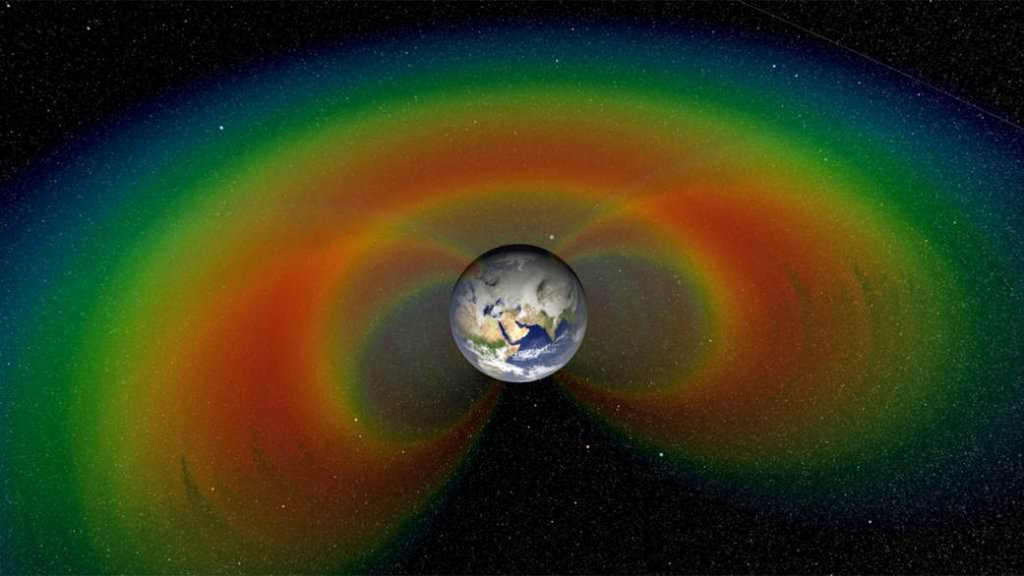
Van Allen Belts
A Van Allen radiation belt is a zone of energetic charged particles, most of which originate from the solar wind, that are captured by and held around a planet by that planet's magnetosphere. Earth has two such belts, and sometimes others may be temporarily created. The belts are named after James Van Allen, who is credited with their discovery. Earth's two main belts extend from an altitude of about 640 to 58,000 km above the surface, in which region radiation levels vary. Most of the particles that form the belts are thought to come from solar wind and other particles by cosmic rays. By trapping the solar wind, the magnetic field deflects those energetic particles and protects the atmosphere from destruction. The belts are in the inner region of Earth's magnetic field. The belts trap energetic electrons and protons. Other nuclei, such as alpha particles, are less prevalent.