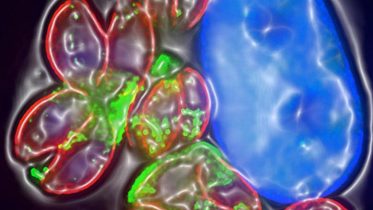
Toxoplasma
Toxoplasma gondii is an obligate intracellular parasitic protozoan that causes toxoplasmosis. Found worldwide, T. gondii is capable of infecting virtually all warm-blooded animals, but felids, such as domestic cats, are the only known definitive hosts in which the parasite may undergo sexual reproduction. T. gondii has been shown to alter the behavior of infected rodents in ways that increase the rodents' chances of being preyed upon by felids. Support for this "manipulation hypothesis" stems from studies showing that T. gondii-infected rats have a decreased aversion to cat urine. Because cats are the only hosts within which T. gondii can sexually reproduce to complete and begin its lifecycle, such behavioral manipulations are thought to be evolutionary adaptations that increase the parasite's reproductive success. Rats that do not avoid cats' habitations will more likely become cat prey.