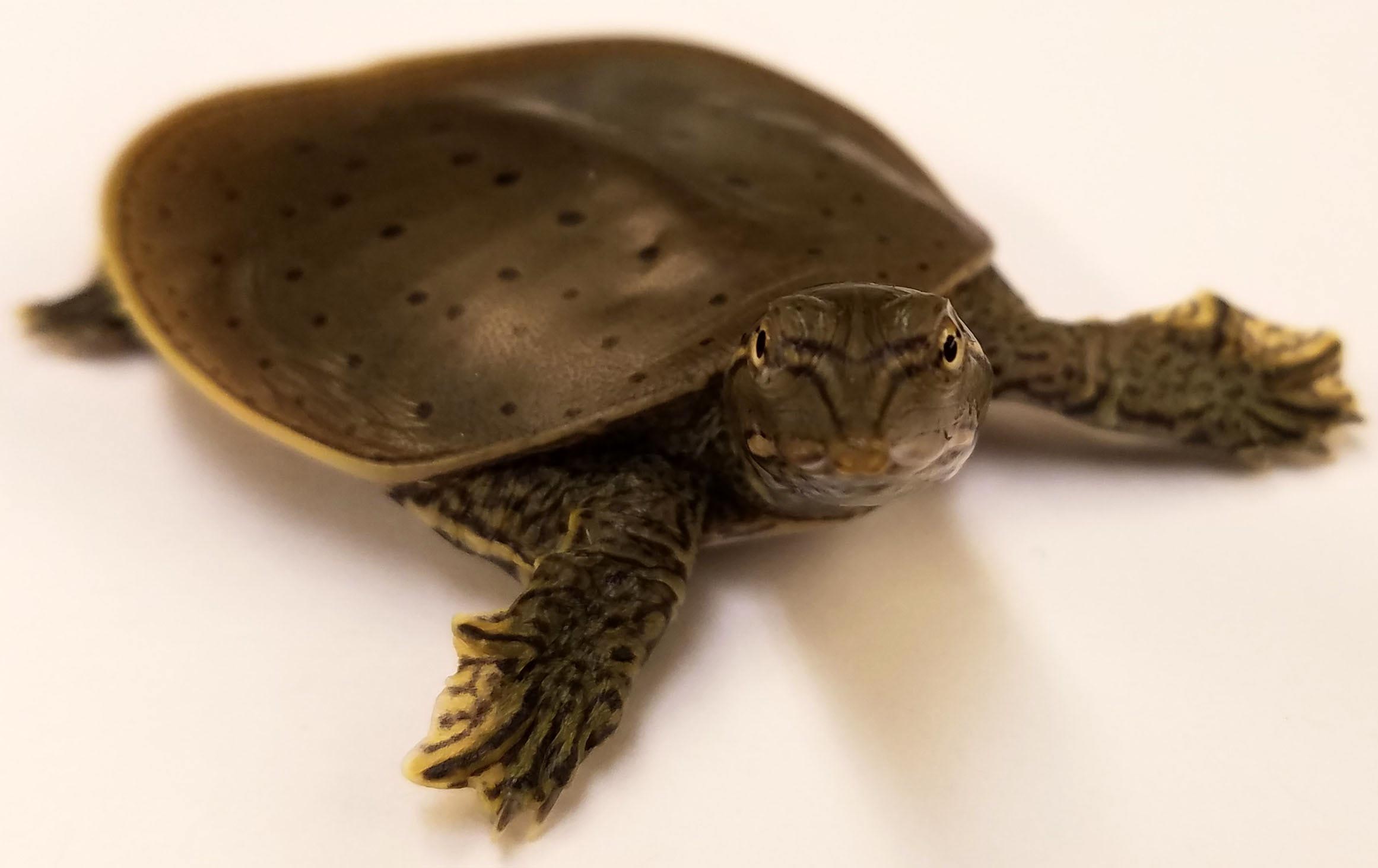
Sex Chromosomes
An allosome is a chromosome that differs from an ordinary autosome in form, size, and behavior. The human sex chromosomes, a typical pair of mammal allosomes, determine the sex of an individual created in sexual reproduction. Autosomes differ from allosomes because autosomes appear in pairs whose members have the same form but differ from other pairs in a diploid cell, whereas members of an allosome pair may differ from one another and thereby determine sex.