Molecular Biology
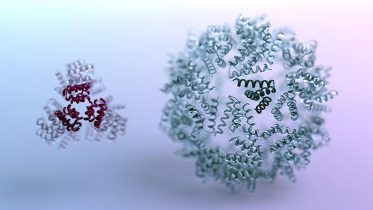
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including molecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. Molecular biology was first described as an approach focused on the underpinnings of biological phenomena - uncovering the structures of biological molecules as well as their interactions, and how these interactions explain observations of classical biology. Molecular biology is not simply the study of biological molecules and their interactions; rather, it is also collection of techniques developed since the field's genesis which have enabled scientists to learn about molecular processes. One notable technique which has revolutionized the field is the polymerase chain reaction, which was developed in 1983. PCR is a reaction which amplifies small quantities of DNA, and it's used in many applications across scientific disciplines, as will be discussed later.