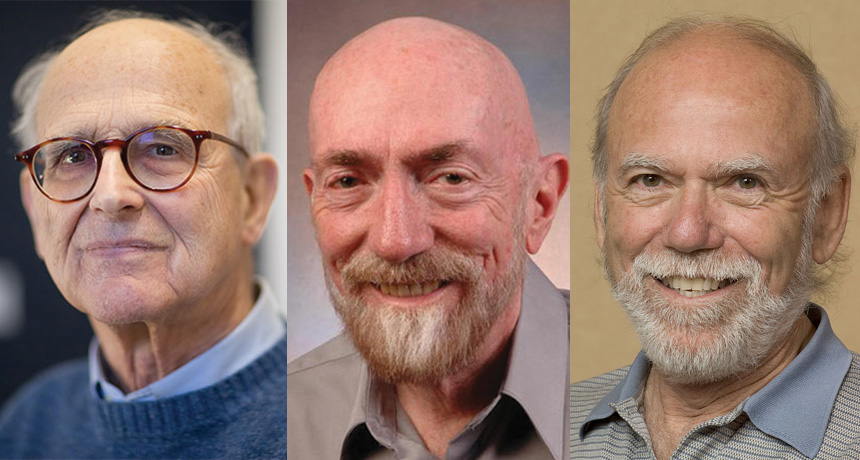
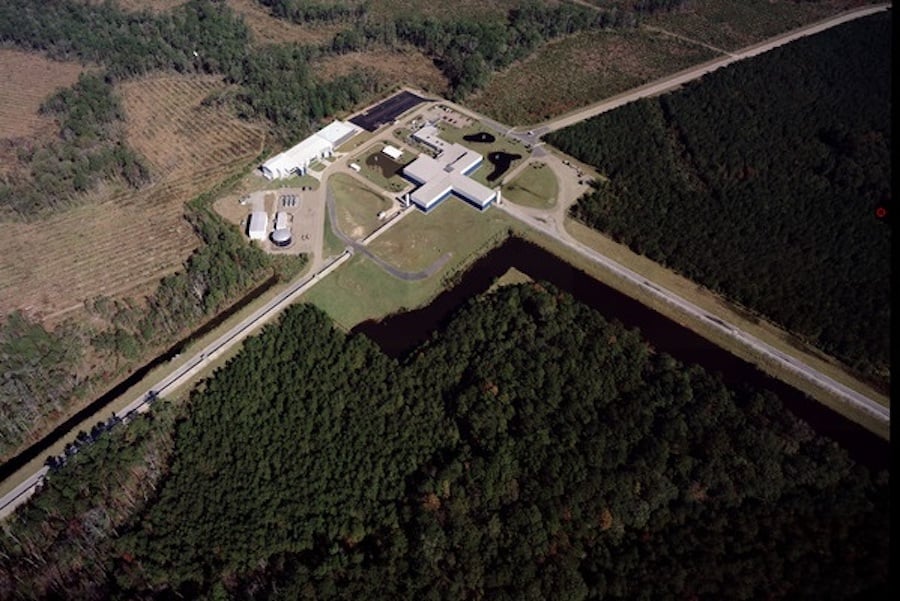
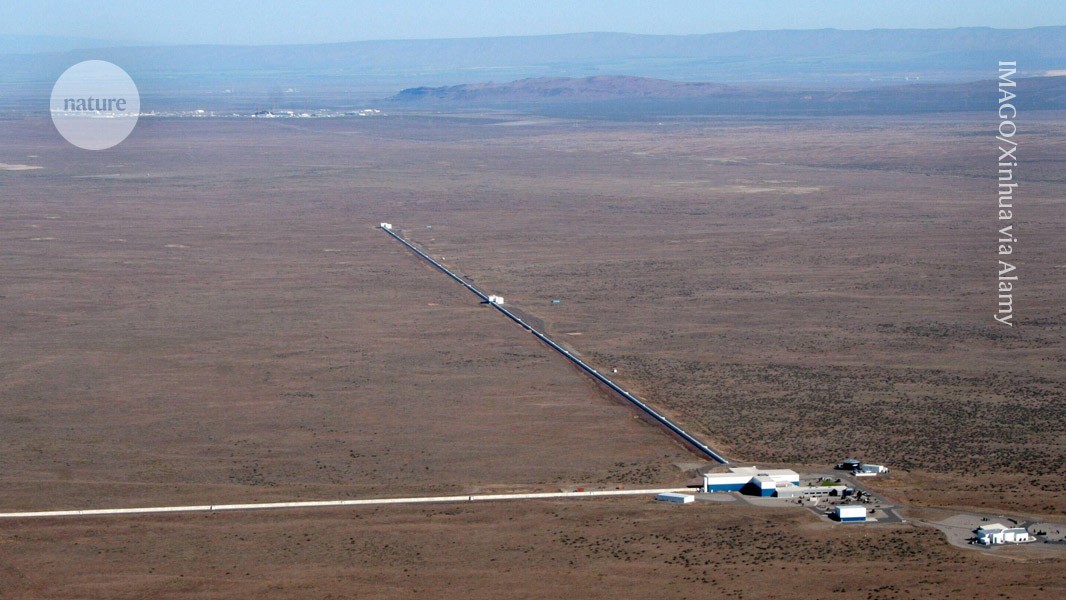
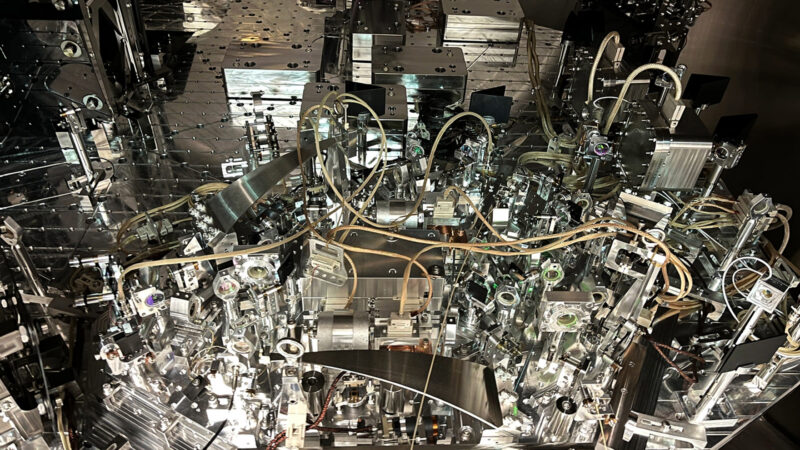
LIGO
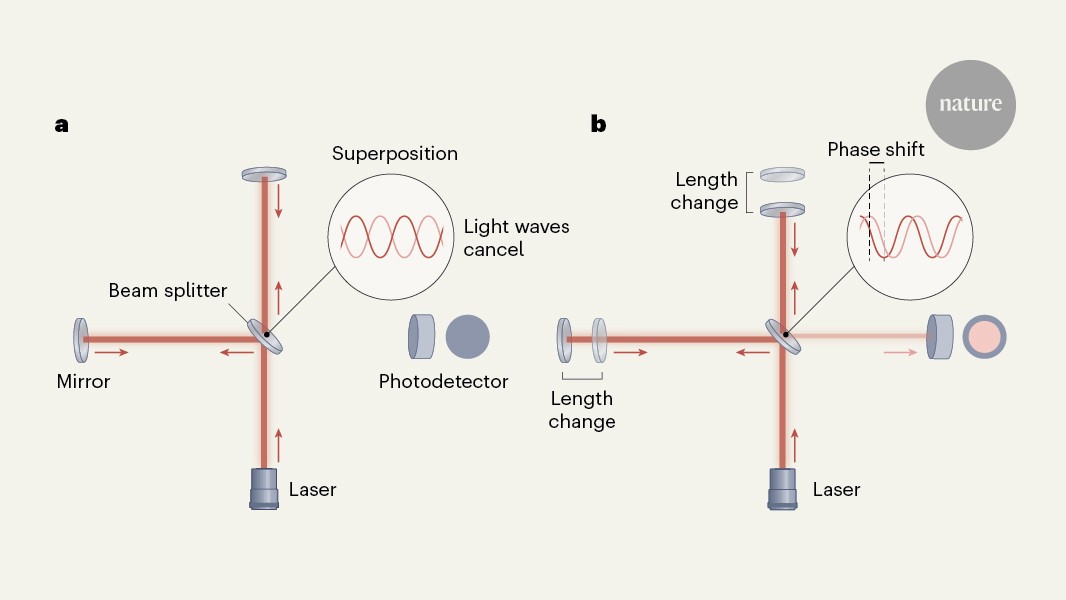
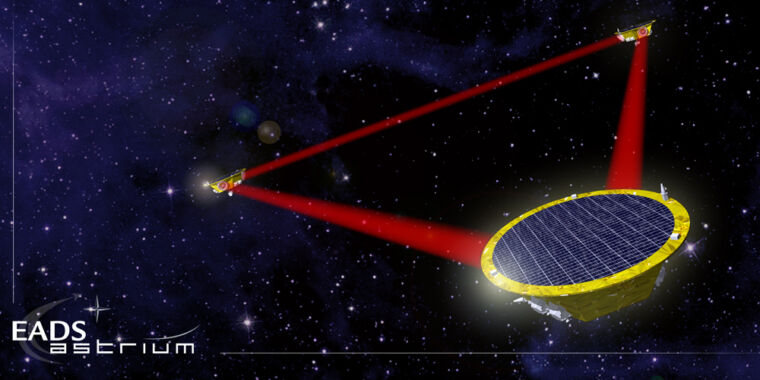
The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory is a large-scale physics experiment and observatory designed to detect cosmic gravitational waves and to develop gravitational-wave observations as an astronomical tool. Two large observatories were built in the United States with the aim of detecting gravitational waves by laser interferometry. These observatories use mirrors spaced four kilometers apart which are capable of detecting a change of less than one ten-thousandth the charge diameter of a proton. The initial LIGO observatories were funded by the United States National Science Foundation and were conceived, built and are operated by Caltech and MIT. They collected data from 2002 to 2010 but no gravitational waves were detected.