Global Population
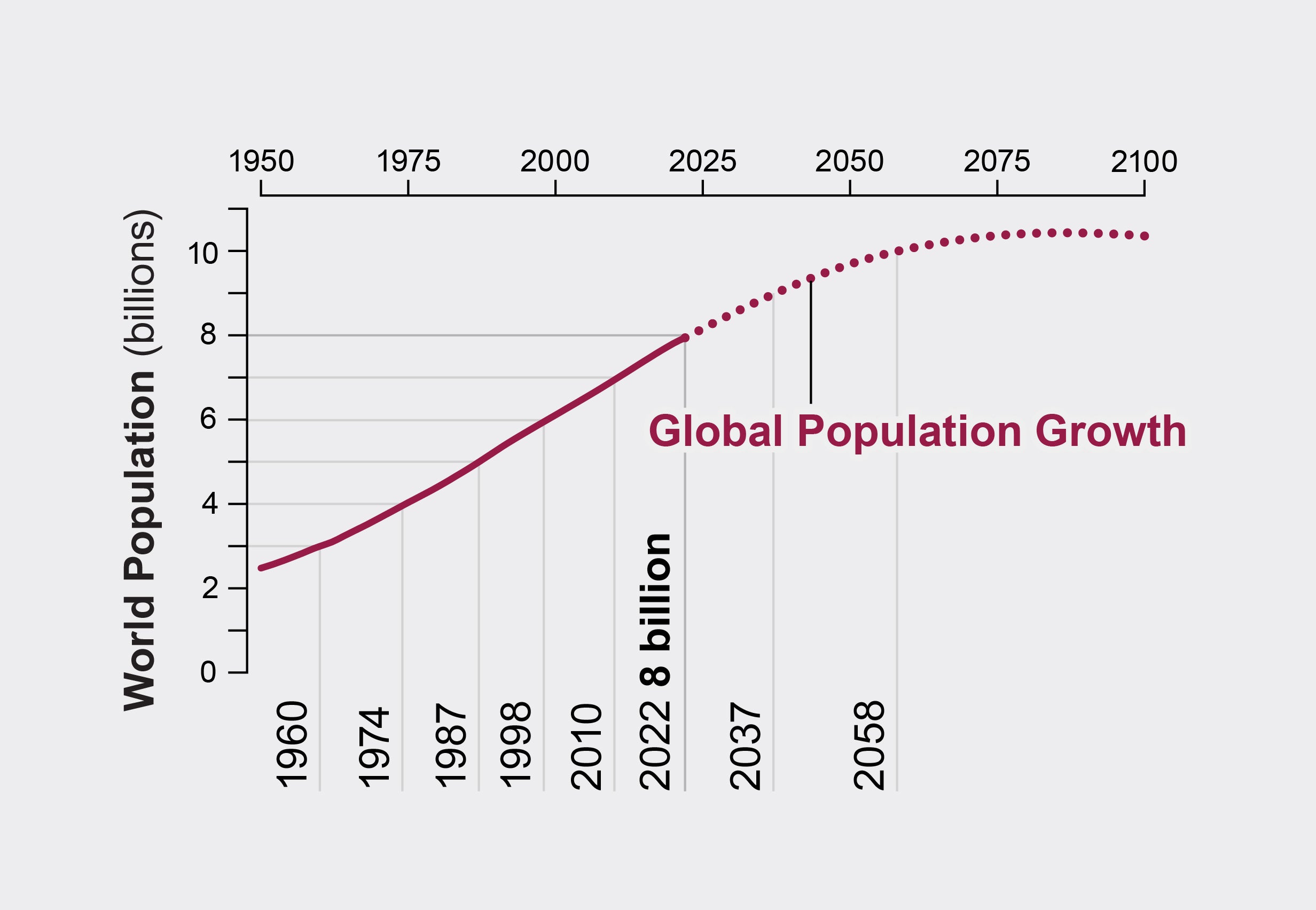
In demographics, the world population is the total number of humans currently living. It was estimated by the United Nations to have exceeded 8 billion in November 2022. It took over 200,000 years of human prehistory and history for the human population to reach one billion and only 219 years more to reach 8 billion. The human population experienced continuous growth following the Great Famine of 1315–1317 and the end of the Black Death in 1350, when it was nearly 370,000,000. The highest global population growth rates, with increases of over 1.8% per year, occurred between 1955 and 1975, peaking at 2.1% between 1965 and 1970. The growth rate declined to 1.1% between 2015 and 2020 and is projected to decline further in the 21st century. The global population is still increasing, but there is significant uncertainty about its long-term trajectory due to changing fertility and mortality rates.