Denisovans
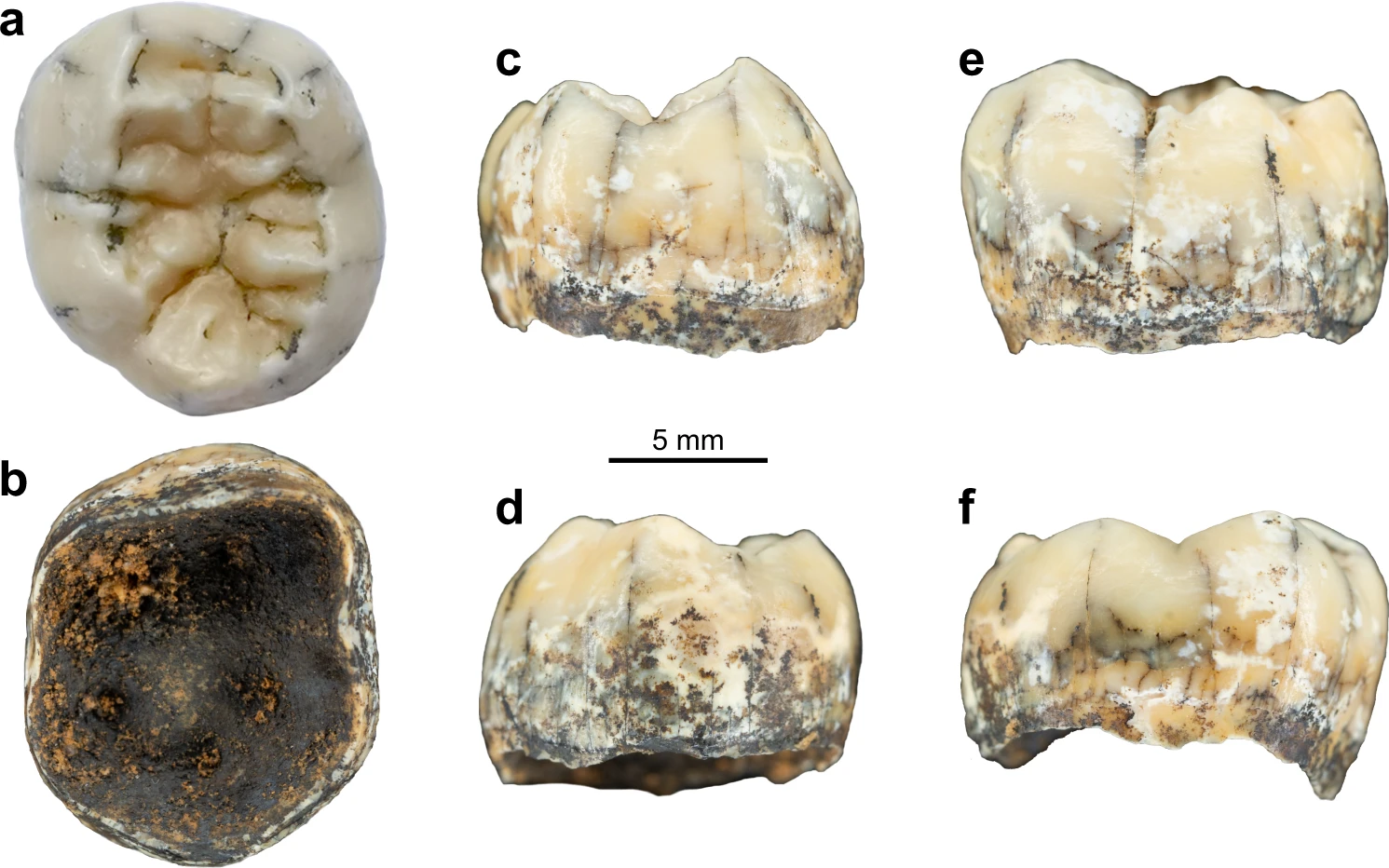
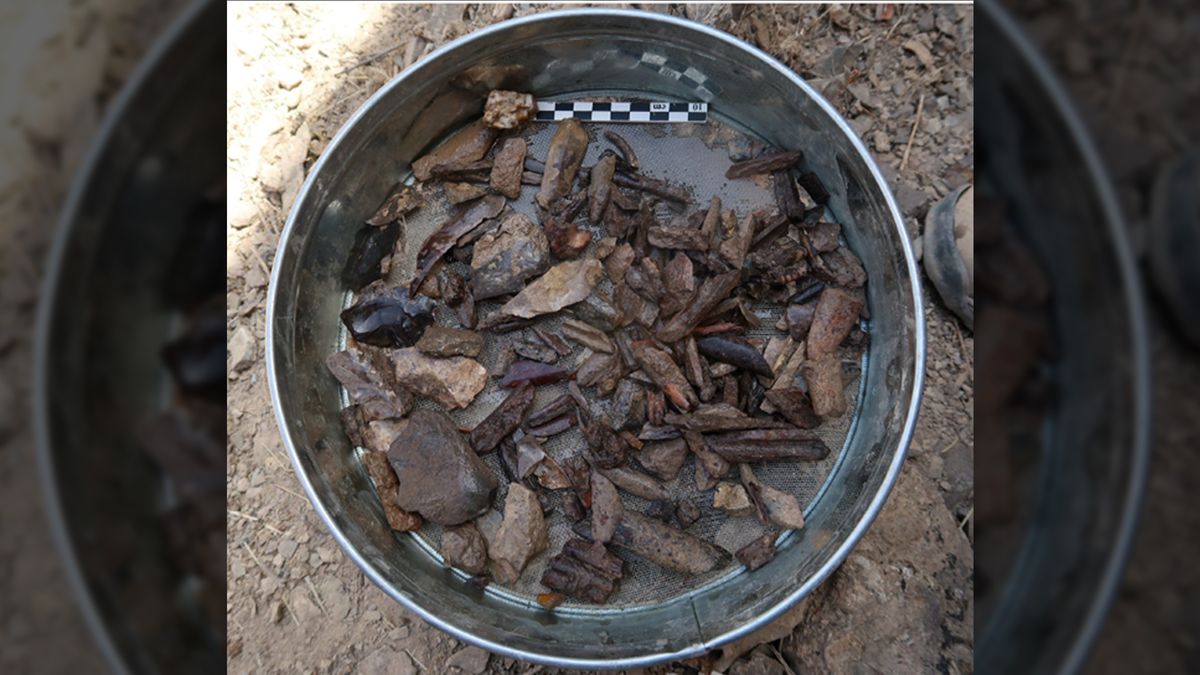
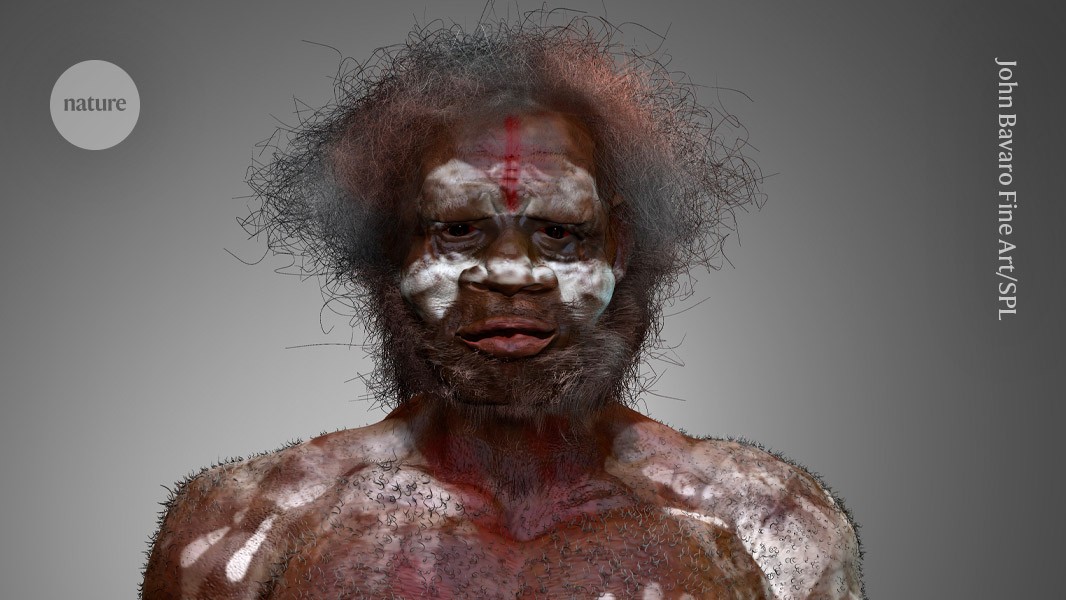
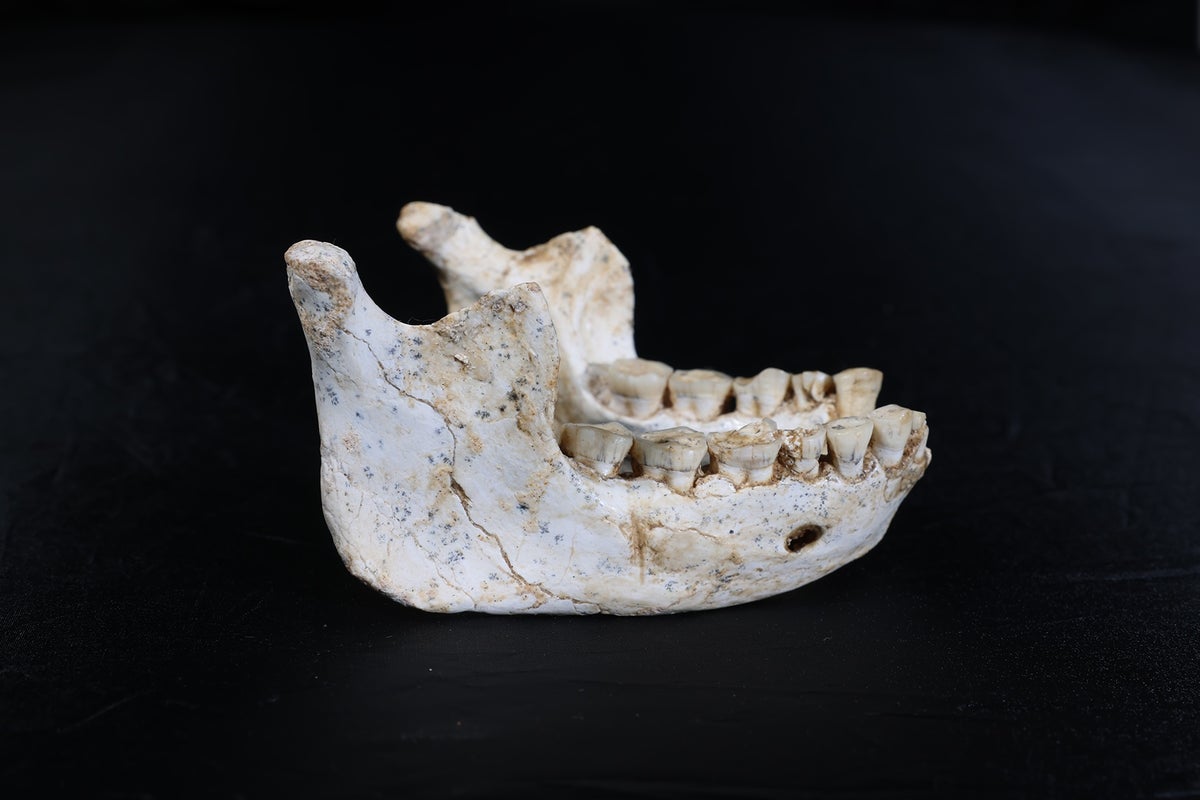
The Denisovans or Denisova hominins are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human that ranged across Asia during the Lower and Middle Paleolithic. Denisovans are known from few physical remains and consequently, most of what is known about them comes from DNA evidence. No formal species name has been erected pending more complete fossil material. The first identification of a Denisovan individual occurred in 2010, based on mitochondrial DNA extracted from a juvenile female finger bone excavated from the Siberian Denisova Cave in the Altai Mountains in 2008. Nuclear DNA indicates close affinities with Neanderthals. The cave was also periodically inhabited by Neanderthals, but it is unclear whether Neanderthals and Denisovans ever cohabited in the cave. Additional specimens from Denisova Cave were subsequently identified, as was a single specimen from the Baishiya Karst Cave on the Tibetan Plateau in China.







 in the Altai Mountains in Siberia.jpg)