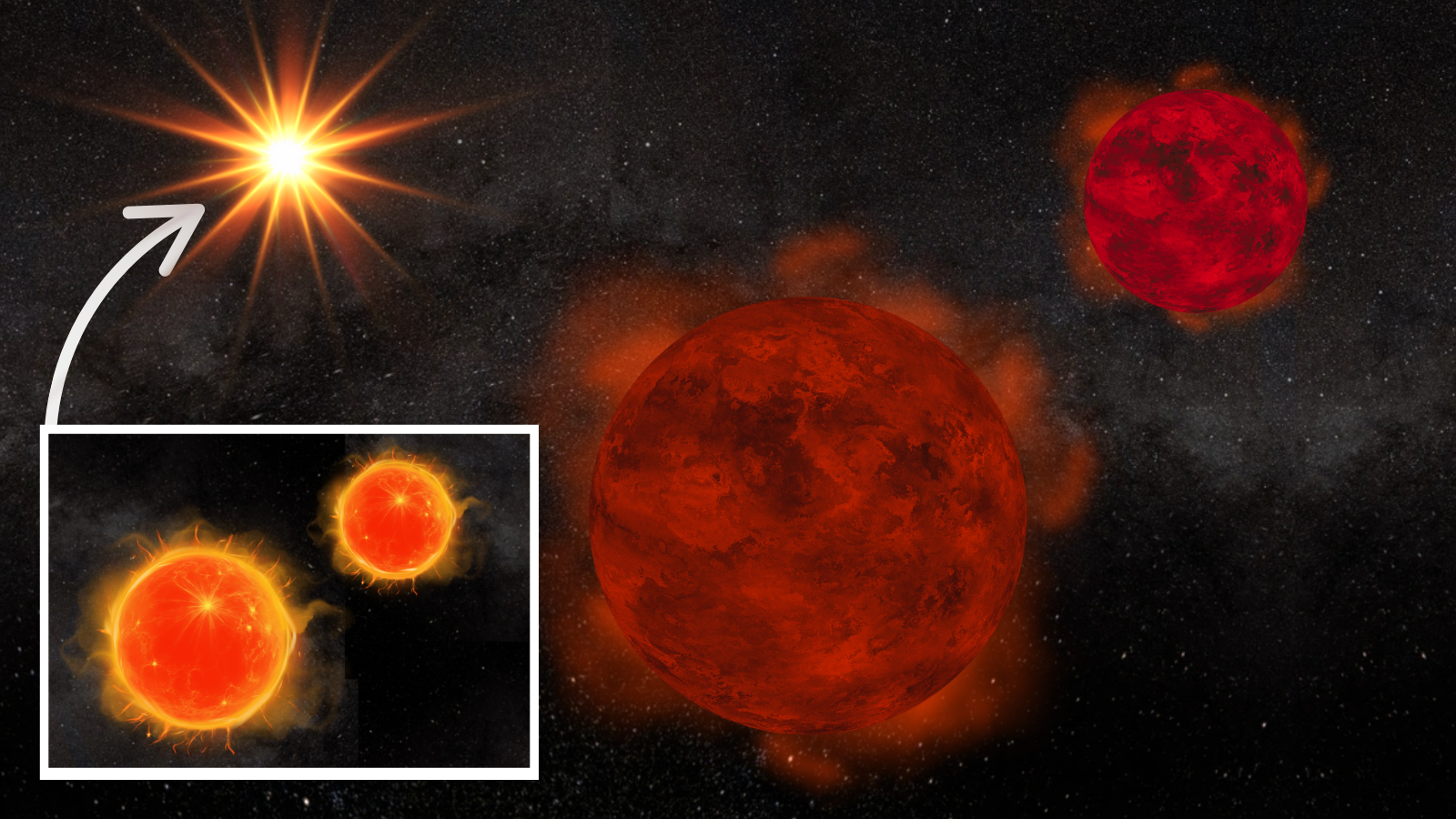
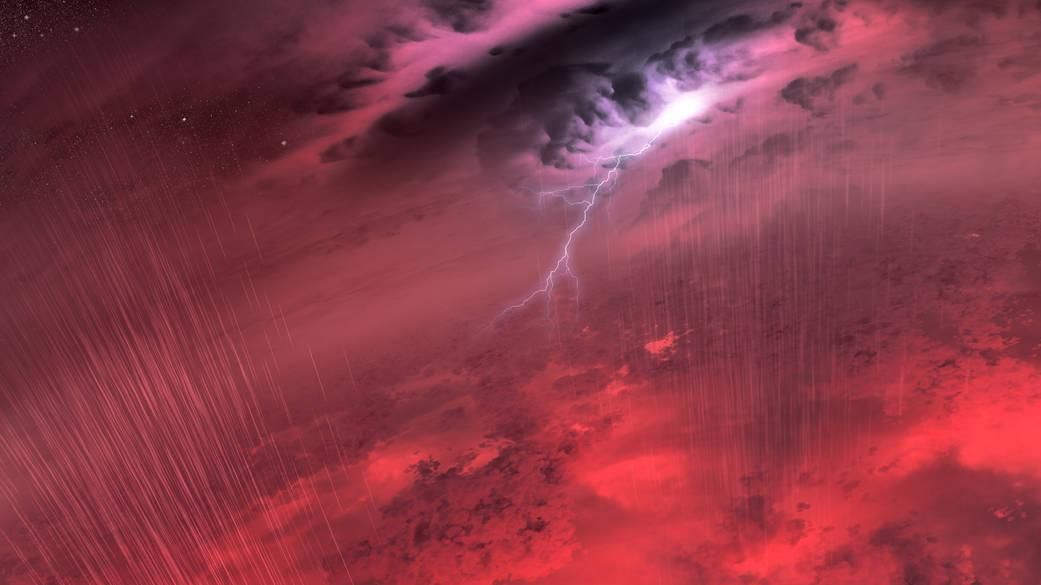
Brown Dwarfs
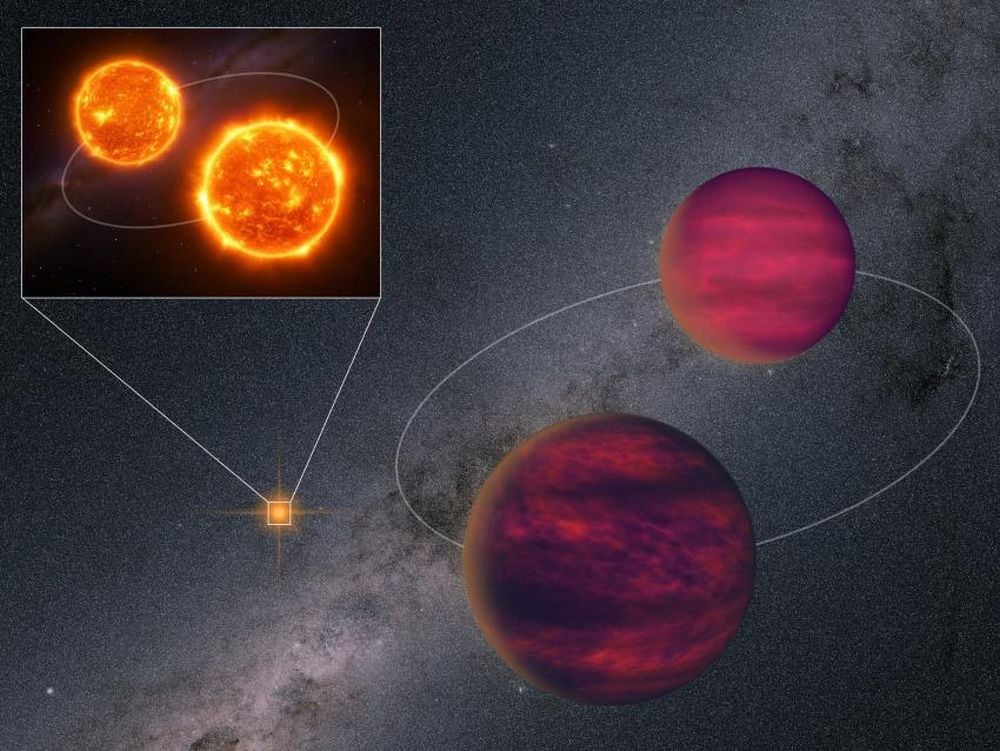
Brown dwarfs are substellar objects that are not massive enough to sustain nuclear fusion of ordinary hydrogen into helium in their cores, unlike a main-sequence star. Instead, they have a mass between the most massive gas giant planets and the least massive stars, approximately 13 to 80 times that of Jupiter. However, they can fuse deuterium, and the most massive ones can fuse lithium. Astronomers classify self-luminous objects by spectral class, a distinction intimately tied to the surface temperature, and brown dwarfs occupy types M, L, T, and Y. As brown dwarfs do not undergo stable hydrogen fusion, they cool down over time, progressively passing through later spectral types as they age. Despite their name, to the naked eye, brown dwarfs would appear in different colors depending on their temperature. The warmest ones are possibly orange or red, while cooler brown dwarfs would likely appear magenta to the human eye.