Alps
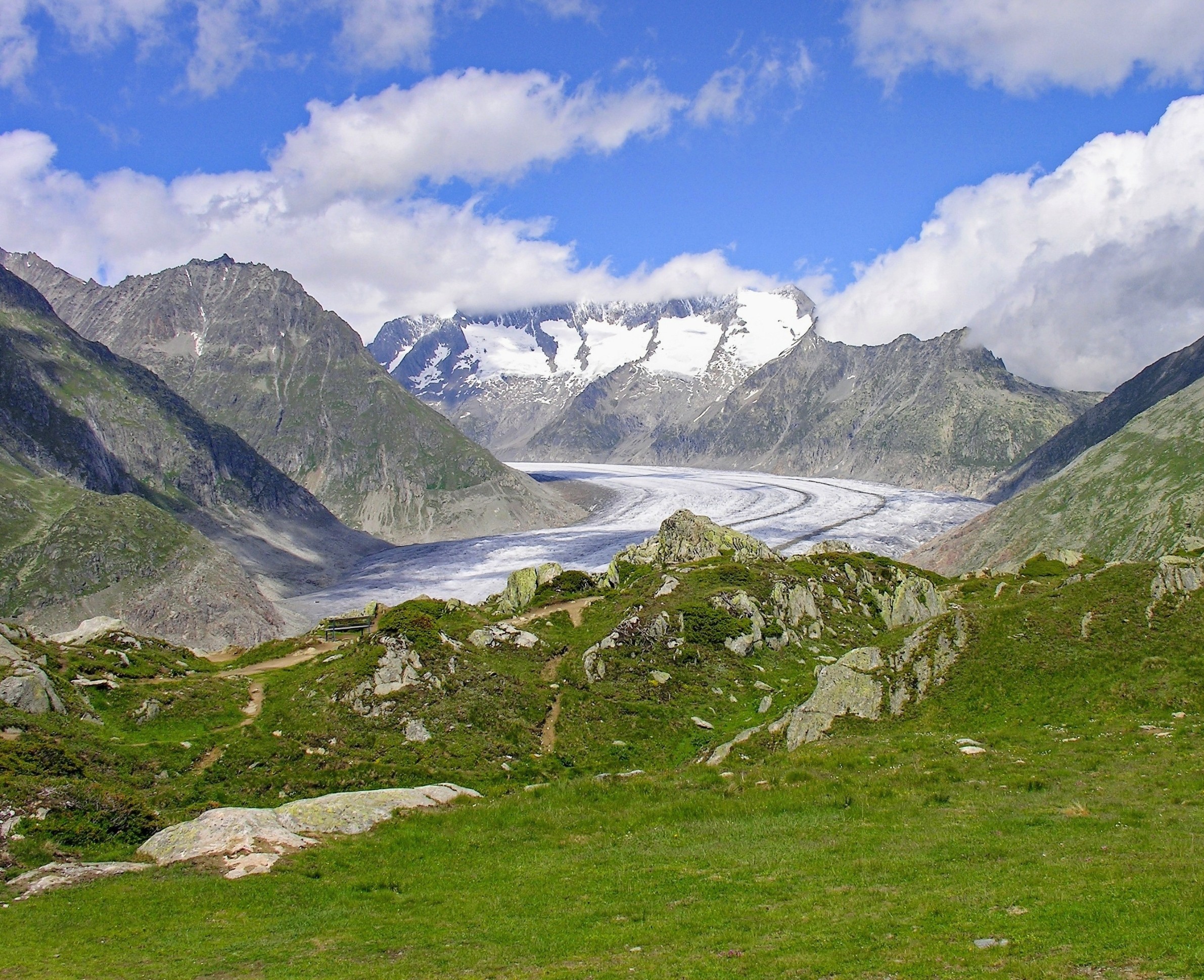
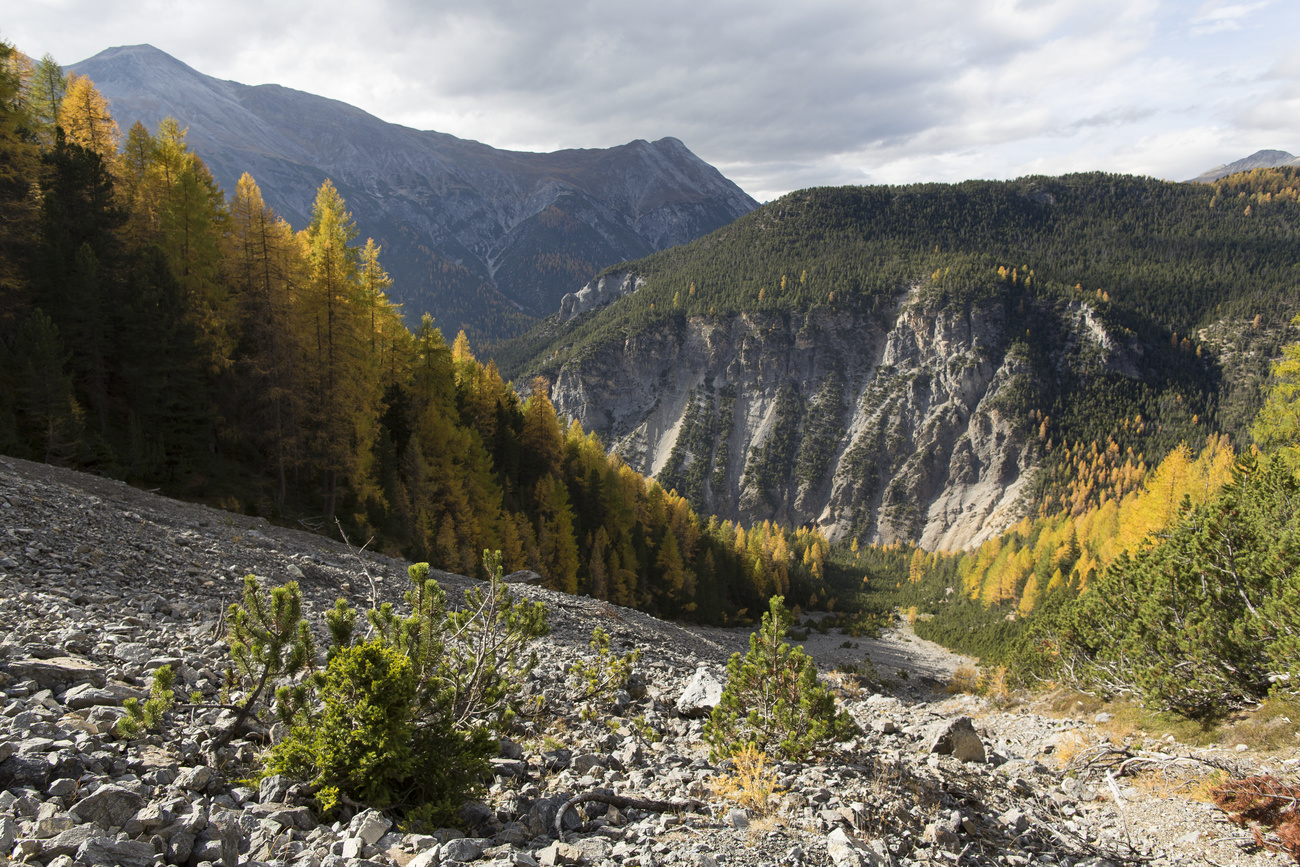
The Alps are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately 1,200 km across seven Alpine countries: France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, and Slovenia. The Alpine arch generally extends from Nice on the western Mediterranean to Trieste on the Adriatic and Vienna at the beginning of the Pannonian Basin. The mountains were formed over tens of millions of years as the African and Eurasian tectonic plates collided. Extreme shortening caused by the event resulted in marine sedimentary rocks rising by thrusting and folding into high mountain peaks such as Mont Blanc and the Matterhorn. Mont Blanc spans the French–Italian border, and at 4,809 m is the highest mountain in the Alps. The Alpine region area contains 128 peaks higher than 4,000 m. The altitude and size of the range affect the climate in Europe; in the mountains, precipitation levels vary greatly and climatic conditions consist of distinct zones.