Ocean
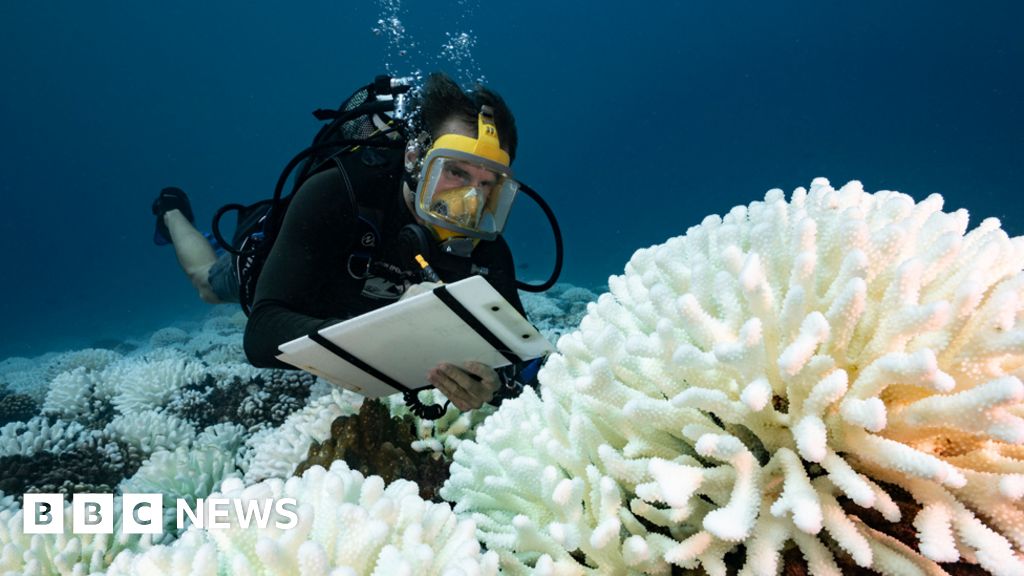
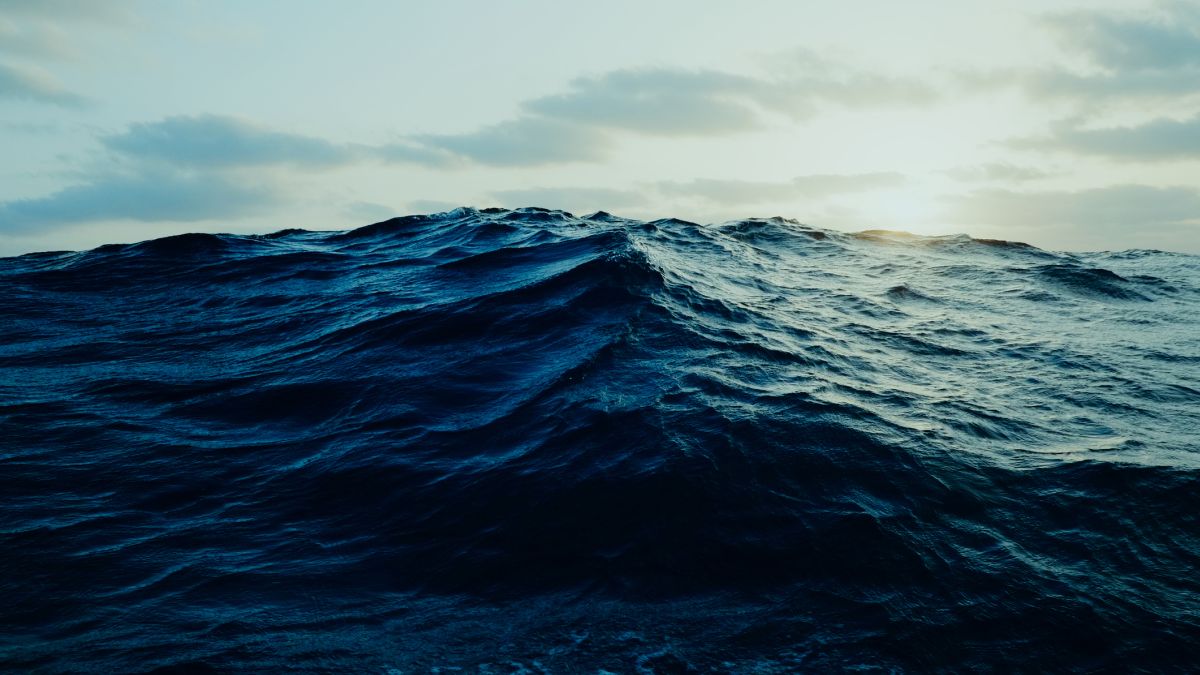
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the world ocean is conventionally divided. Separate names are used to identify five different areas of the ocean: Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Antarctic/Southern, and Arctic. Seawater covers approximately 361,000,000 km² of the planet. The ocean is the principal component of Earth's hydrosphere, and therefore integral to life on Earth. Acting as a huge heat reservoir, the ocean influences climate and weather patterns, the carbon cycle, and the water cycle. Oceanographers divide the ocean into different vertical and horizontal zones based on physical and biological conditions. The pelagic zone consists of the water column from surface to ocean floor throughout the open ocean. The water column is further categorized in other zones depending on depth and on how much light is present.