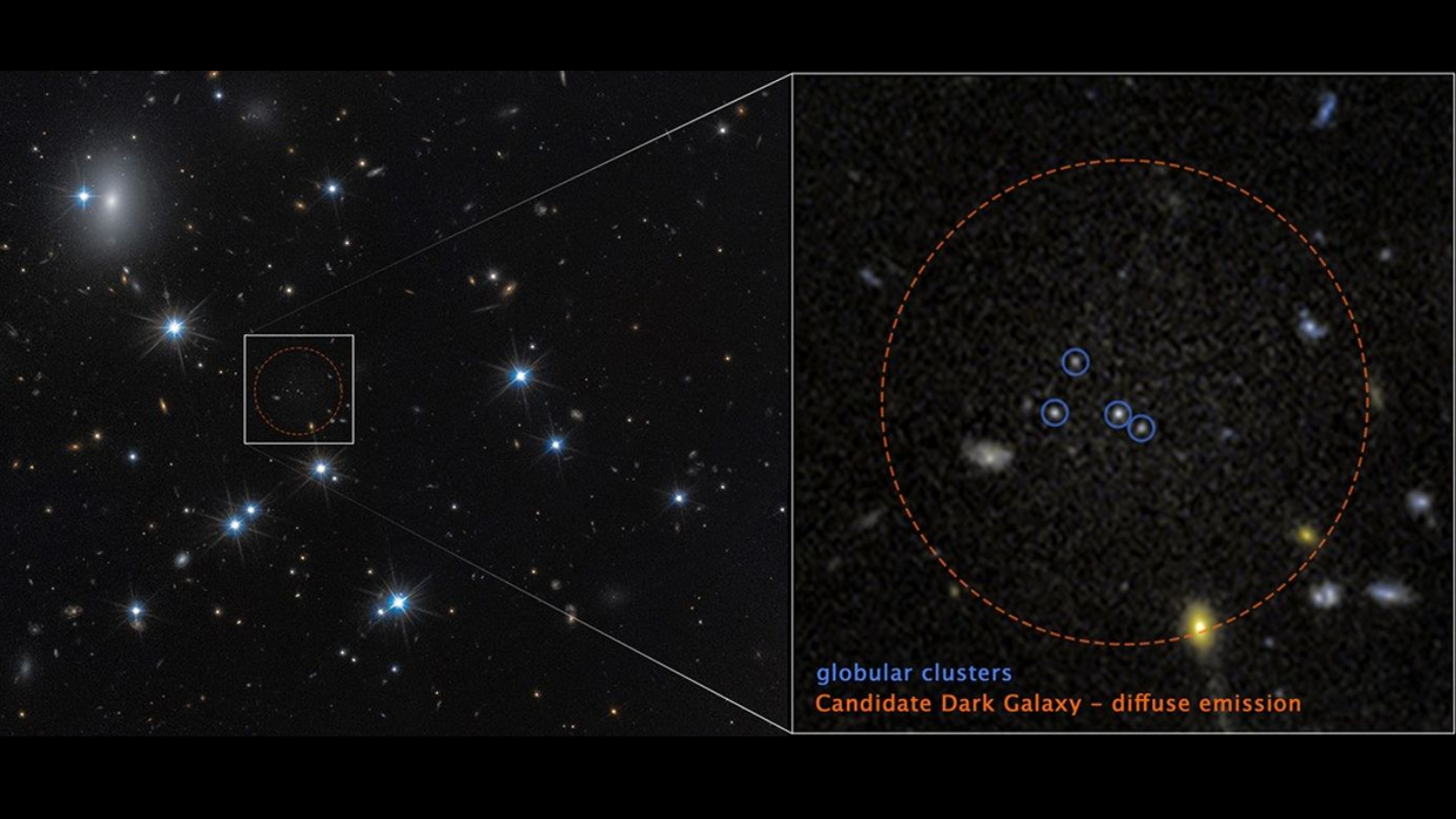
Dark Matter
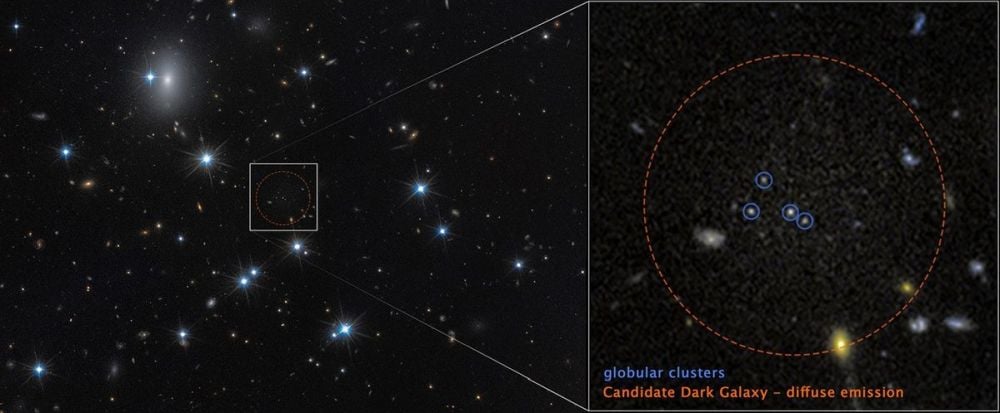
Dark matter is a hypothetical form of matter thought to account for approximately 85% of the matter in the universe. Dark matter is called "dark" because it does not appear to interact with the electromagnetic field, which means it does not absorb, reflect, or emit electromagnetic radiation and is, therefore, difficult to detect. Various astrophysical observations – including gravitational effects which cannot be explained by currently accepted theories of gravity unless more matter is present than can be seen – imply dark matter's presence. For this reason, most experts think that dark matter is abundant in the universe and has had a strong influence on its structure and evolution. The primary evidence for dark matter comes from calculations showing that many galaxies would behave quite differently if they did not contain a large amount of unseen matter. Some galaxies would not have formed at all and others would not move as they currently do.